Introduction
Entrepreneurship involves creation of a new enterprise and assuming all the risks involved to make a profit. A person has to uphold entrepreneurial characteristics to succeed in the business venture. They ensure that production factors, such as labor, land, capital, and raw materials, are available and well organized to guarantee that the business venture is running. The entrepreneur can incorporate different leadership approaches and styles to influence business performance. To manage a business hard work and constant monitoring of employees is needed to meet business targets and profit. Various elements characterize entrepreneurship: it is an economic activity, involving the use of creativity and innovation, risk bearing, and finally making a profit.
Entrepreneurship and Leadership Approaches and Styles
For the entrepreneur to ensure that the businesses make a profit and operate effectively and efficiently, different approaches and leadership styles have to be adopted. The leadership styles and approaches used in an organization promote innovativeness and creativity in an organization due to strict policies developed, standards set, and norms established (Bagheri & Akbari, 2018). There are five leadership styles commonly used in organizations with their own impact on organization performance (Chin et.al., 2019).
These five leadership styles are: transactional, autocratic, laissez-faire, democratic, and transformational leadership. Democratic and transformational leadership styles have similar qualities and content, which encourage entrepreneurial features of autonomy, risk-bearer, creativity, and innovativeness (Pollman & Barry, 2016). These two leadership styles ensure the organization’s capacity and entrepreneurial orientation tendency. This paper analyzes the impact of various leadership styles that have their impact on the organization’s behavior, whether the style encourages or limits entrepreneurial activities and changes the organization’s behavior.
Leadership, as a concept, fulfils a number of roles in a professional environment. Leadership revolves around identifying a purpose, goal, and objective, possessing the ability to influence others which might be manipulative and persuasive (Lyons & Schneider, 2019). It can be understood that leadership involves sharing ideas and socializing with others. The first style of management discussed is autocratic leadership.
According to Lewin, an autocratic leader focuses on attaining organizational goals despite internal or external distractions. Therefore, the leader using this style is efficient and effective and ensures their subordinates deliver goals and meet deadlines as stated (George & Scheeper, 2017). In addition, coordination and control in the organization are strict. In this leadership style, it means that staff is limited to exploit their potential and talents as a result of strict policies.
The second leadership style is the democratic one. The approach focuses on sharing responsibilities, and subordinate staffs are appreciated for their contribution to organizational goals and objectives. However, this style of leadership in regards to staff is shown to be less productive than an autocratic approach of leadership (McKeever, 2016). Although they were more substantial because they had freedom of expression of their ideas, creativity, and views when undertaking their tasks and other roles. It has such drawbacks as a slow decision-making process, delays, and failure to meet goal deadlines because of a lot of consultation and inter-dependence of roles.
The third form of leadership style used in an organization is the Laissez-Faire syle which offers a lot of freedom to its lower subordinate staff, making the leader lose control in managing the junior staff. According to Bass and Riggio, (2006), leadership is destructive because the leader has no power to coerce the subordinate staff and control them. On the contrary, they support these leadership styles because subordinate employees have work flexibility and are useful since they have freedom of expression.
The fourth leadership style is a transactional leadership style derived from the word transaction, which indicates how the leader relates with their followers. This relationship between the employer and employee is entirely defined, and roles are stated according to the agreed forms of compensation and contribution (Al Khajeh, 2018). This leadership style is controlling and indicates the policies and forms of work techniques and methods that need to be followed.
The last fifth and last form of leadership style applied in an organization and influences behavior is the transformational leadership style. This style is perfect and rewarding because both the leader and the follower enjoy certain benefits (Goodnight, 2017). It encourages and supports subordinate staff to develop in different aspects, such as intellectually, ideally, and their talents since they are inspired and motivated. Leaders benefit from this form of style because trust is developed, loyalty is built, and workers’ creativity is improved. In summary, we can say the form of leadership style used can significantly impact an organizational performance since every style has its benefits and drawbacks.
Organizations should choose the best leadership style to achieve their set goals and objectives. However, of all the five leadership styles transformational leadership styles, the recommended forms of leadership are transformational and democratic (Alkahtani, 2016). This because they are very impactful and supportive when it comes to entrepreneurial orientation. These two leadership forms are geared towards attaining organizational goals and allowing workers to participate and contribute their ideas to the organization (O’Brien & Hamburg, 2019). Besides, these forms ensure that workers efforts are rewarded, and their innovativeness and creativity is recognized hence ensuring efficiency and effectiveness in the organization
Great Entrepreneurs: Entrepreneurial Skills and Attributes
To ensure business success, various entrepreneurial skills and attributes have to be adopted and implemented to be successful. The entrepreneurial skills that have to be incorporated in the business enterprise include technical, business management, and personal skills (Obeidat & Tarhini, 2016). Bill Gates is a great software developer who has illustrated great technical skills, Technical skills involve the entrepreneur’s capability to produce, develop a business network, ensure a friendly business environment, adapt to new business trends, and have good interpersonal skills. The entrepreneur should also possess good business management skills (Obeidat & Tarhini, 2016).
This involves all the activities which occur in the business enterprise starting from planning, marketing, and sourcing for finances, setting business objectives and goals, and decision making. Mark Zuckerberg, the founder of Facebook, has high levels of managerial skills and good planning which has contributed to the great wealth acquisition (Papia, 2020). Lastly, individuals possess personal attributes, which are crucial for any business success. Which include confidence, honesty, persistence, vision, innovativeness, and many more (Newman et.al., 2018). One of the better example for many of these traits is Steve Jobs, who is well-known in the field of modern tech.
The man has had a remarkable passion and charisma, as well as a clear vision of what he wanted to achieve in his career (Henson). These skills are critical as much as the business is to be well organized. If an entrepreneur does not have good personal skills, the business will automatically fail. One should tend to creativity, which will help him/her solve problems and adapt to challenges in the working environment (Harrison et.al., 2016). Taking calculated risk acts as a shock absorber, and the entrepreneur does not make decisions that could adversely affect the business. An attribute of locus control will help an entrepreneur have self-confidence and be opportunistic on business ideas and opportunities to propel the business (Deschamps et al, 2016). Every business needs to have a business plan to operate efficiently and effectively.
A business plan can be defined as a detailed description of a business stating its objectives, strategies, goals, executive team, and finances. In developing a business plan, two elements should be considered: the marketing position statement and the Unique Selling Proposition. A marketing statement states the problem the business will solve with its products (Leitch & Volery, 2017). In contrast, a Unique Selling Proposition states how the business product is unique from other substitute products in the market.
A business has to know its target market or audience regarding its age, demographic characteristics, and psychographic features. This will affect the business to concentrate hence saving its marketing cost. The business has to understand the five forces that influence business operations (McKeever, 2016). These factors include existing competitors, the presence of substitute products in the market, the emergence of new competitors, bargaining power of its suppliers and customers. A business requires to create a competitive strategy from its competitors, which includes cost leadership, differentiation, and focus.
Lastly, there is a need for a business to project its financial performance in terms of expected cash the company expects to get from sales and its customers (Harrison et.al., 2018). If a business has precise financial projections, it can attract investors because of its high profitability. For any business plan to be viable, the business has to consider all those factors to stand out in the market compared to its competitors.
There is a need to develop a business plan whereby the school targets young people who would like to earn skills to be highly employable. Therefore, the school’s fees are subsidized and affordable compared to other colleges (Andriani et al., 2018). The College has well-trained tutors and finds its students jobs and internships after completing College in these cases, the business marketing statement helps needy students acquire a college education. On the other hand, the Unique Selling Proposition is the affordable tuition fee and job and internship placement of students. The unique selling proposition makes the College standout compared to its competitors.
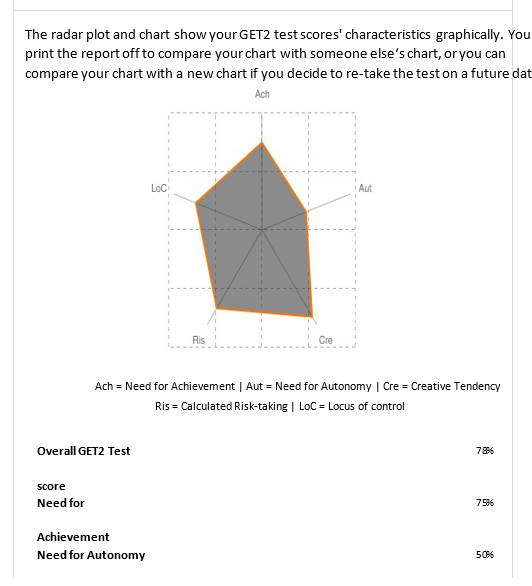
Reflection on the GET-test Alive (Creativity test) and Leadership test
My G-test score was an overall of 78 percent a represented my overall entrepreneurship skills reflecting on my ability to become an entrepreneur. My best score was on creativity tendency which scored 92%, an illustration that I am a creative entrepreneur and that’s my major strength. Creativity can help tremendously with both planning and problem solving, and I think it is one of the most essential qualities for a good leader/entrepreneur.
It can allow one to find unexpected solutions to ever-emerging issues and also move in fresh directions in the effort to push their business forward. My achievement and need for autonomy were 50% which meant that I needed to work on my leadership and managerial skills to provide a good business environment for my employees. The need for autonomy manifests in my difficulty of making decisions on my own, and I have to further work on relying on myself more in my decision-making process. I think I will be able to acquire the needed skills in time, by practicing and gaining experience in the field of entrepreneurship.
Strong leadership qualities are essential for running a successful business and being independent. The entrepreneur is innovative, inventive, and artistic, and this characteristic will help the business enterprise succeed despite internal and external market forces (Al Mamun et.al., 2018). A high score on risk-taking tendency shows that one can utilize information and project results. Risk taking is both dangerous and essential, as it allows one to get in front of the competition and become a leading actor in the business scene. A person sets challenging but attainable goals, and this tendency is essential for an entrepreneur to be successful in a competitive environment (Orabi, 2016).
Goal setting as a process gives the businessman to carefully consider their steps and act in accordance with both the needs of the company and their own perceptions of beneficial strategy. By carefully planning the steps ahead of time, a good leader creates a stable framework for his helpers and followers. Lastly, the locus of control is significant in developing an enterprise because an entrepreneur needs to be self-confident, determined, and aggressive to rely on business partners, suppliers, and clients entirely. Control is important in all aspects of business, be it management or development of new approaches. The ability to take into consideration the variety of factors presented to you and account for any future developments is a sign of a good leader.
Conclusion
In conclusion, an entrepreneur needs to embrace all the tendencies of a successful business person and cultivate them to succeed in their business. By finding inspiration in other successful people and fully understanding what kinds of traits are necessary to become as good as them, a beginner has an opportunity to grow in both a personal and in a business sense. Developing and improving entrepreneur attributes is crucial for any entrepreneur who wants to start and run a successful enterprise.
The success of one’s endeavors largely determines both their current strategy and their options for future development. To best serve one’s own needs and the needs of their workers, a business has to be developed successfully. Entrepreneurs’ level of success has leadership performance contributing to the way the entrepreneur relates with workers. Leader worker relations directly affect revenue hence the great need to embrace leadership skills in entrepreneurship.
Appendix 1

Appendix 2
Leadership Styles Questionnaire
Purpose
- To identify your style of leadership.
- To examine how your leadership style relates to other styles of leadership.
Directions
- For each of the statements below, circle the number that indicates the degree to which you agree or disagree.
- Give your immediate impressions. There are no right or wrong answers.
Scoring
- Sum the responses on items 1, 4, 7, 10, 13, and 16 (authoritarian leadership).
- Sum the responses on items 2, 5, 8, 11, 14, and 17 (democratic leadership).
- Sum the responses on items 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, and 18 (laissez-faire leadership).
Total Scores
Authoritarian Leadership: 21.
Democratic Leadership: 23.
Laissez-Faire Leadership: 14.
Scoring Interpretation
This questionnaire is designed to measure three common styles of leadership: authoritarian, democratic, and laissez-faire. By comparing your scores, you can determine which styles are most dominant and least dominant in your own style of leadership.
- If your score is 26–30, you are in the very high range.
- If your score is 21–25, you are in the high range.
- If your score is 16–20, you are in the moderate range.
- If your score is 11–15, you are in the low range.
References
Al Khajeh, E. H. (2018). Impact of Leadership Styles on Organizational Performance. Journal of Human Resources Management Research, 2018, 1–10. Web.
Al Mamun, A., Ibrahim, M., Yusoff, M., & Fazal, S. (2018). Entrepreneurial Leadership, Performance, and Sustainability of Micro-Enterprises in Malaysia. Sustainability, 10(5), 1591. Web.
Alkahtani, A. H. (2015). The Influence of Leadership Styles on Organizational Commitment: The Moderating Effect of Emotional Intelligence. Business and Management Studies, 2(1), 23. Web.
Andriani, S., Kesumawati, N., & Kristiawan, M. (2018). The influence of the transformational leadership and work motivation on teacher’s performance. International Journal of Scientific & Technology Research, 7(7), 19-29. Web.
Bagheri, A., & Akbari, M. (2018). The impact of entrepreneurial leadership on nurses’ innovation behavior. Journal of Nursing Scholarship, 50(1), 28-35. Web.
Barry, J. M., & Pollman, E. (2016). Regulatory Entrepreneurship. SSRN Electronic Journal. Web.
Bridge, S. (2017). Is “entrepreneurship” the problem in entrepreneurship education? Education + Training, 59(7/8), 740–750. Web.
Chin, T. L., Yap Peng Lok, S., & Kee Peng Kong, P. (2019). Does Transformational Leadership Influence Employee Engagement. Global Business & Management Research, 11(40-50). Web.
George, R., Chiba, M., & Scheepers, C. B. (2017). An investigation into the effect of leadership style on stress-related presenteeism in South African knowledge workers. SA Journal of Human Resource Management, 15. Web.
Goodnight, R. (2017). Laissez-faire leadership. Encyclopedia of Leadership. Sage Publications. Web.
Harrison, C., Paul, S., & Burnard, K. (2016). Entrepreneurial Leadership: A Systematic Literature Review. International Review of Entrepreneurship, 14, 20-30. Web.
Harrison, R., Leitch, C., & Mcadam, M. (2015). Breaking Glass: Toward a Gendered Analysis of Entrepreneurial Leadership. Journal of Small Business Management, 53(3), 693–713. Web.
Henson, R. The Leadership of Steve Jobs. Rutgers Business School-Newark and New Brunswick. Web.
Justice. Journal of Healthcare Management, 61(3), 194-213. Web.
Leitch, C. M., & Volery, T. (2017). Entrepreneurial leadership: Insights and directions. International Small Business Journal: Researching Entrepreneurship, 35(2), 147–156. Web.
Lyons, J. B., & Schneider, T. R. (2009). The effects of leadership style on stress outcomes. The Leadership Quarterly, 20(5), 737–748. Web.
Masa’deh, R., Obeidat, B. Y., & Tarhini, A. (2016). A Jordanian empirical study of the associations among transformational leadership, transactional leadership, knowledge sharing, job performance, and firm performance. Journal of Management Development, 35(5), 681–705. Web.
McKeever, M. (2016). How to write a business plan. Nolo. Web.
Newman, A., Tse, H. H. M., Schwarz, G., & Nielsen, I. (2018). The effects of employees’ creative self-efficacy on innovative behavior: The role of entrepreneurial leadership. Journal of Business Research, 89, 1–9. Web.
O’Brien, E., & Hamburg, I. (2019). A critical review of learning approaches for entrepreneurship education in a contemporary society. European Journal of Education, 54(4), 525–537. Web.
Orabi, T. G. (2016). The Impact of Transformational Leadership Style on Organizational Performance: Evidence from Jordan. International Journal of Human Resource Studies, 6(2), 89. Web.
Papia, F. A. (2020). Leadership Qualities – Styles, Skills, and Traits of Mark Zuckerberg. The Strategy Watch. Web.

