Pricing Objectives
- Increase market share from 0 to 30% within 6 months of operation
- Increase sales level to 75% within the first 3 months of operation
- To yield 20% profits within the first accounting period.
Detail in price
In a research by Smith (2011), pricing decisions must capture the dynamics that exist in the market. Factors such as competition and customer preferences must be considered when setting the price. It is important to understand that pricing has a direct impact on a company. As an example, wrong pricing leads to loss of revenue, profits, customers and ultimately the collapse of a company.
After considering the situation in sandal market, our company will utilize value based and cost based pricing in different segments. According to Lamb, Hair, and McDaniel (2008), value-based pricing is anchored on quality of products. Through value-based pricing, customers and competition are considered before determining the correct price. This is a strategy used by customer driven firms hence customer attributes are paramount. In contemplation of this strategy, our firm will take into account different needs of our customers. The design, weight, colour, and shape of flip-flops will be critical in pricing out product.
The second pricing strategy that will be applied in our company is cost-based pricing. Ferrell and Pride (2008), assert that cost-based pricing requires the addition of a percentage to the cost of a product. The strategy fails to consider economic situation of supply and demand. In application of this strategy, our firm will add specific percentage to cost of producing flip-flops in low cost segment. One of the rationales for applying the strategy in low-cost segment is that target customers might not show interest in different designs, shapes, and colours of flip-flops. Furthermore, the strategy is intended to earn additional given that price is marked up by a percentage.
Demand and Price Sensitivity
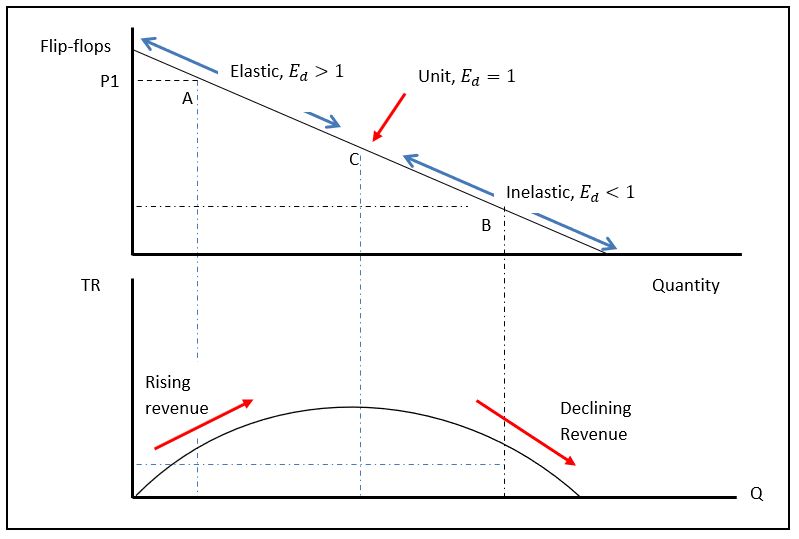
Our product is sensitive to changes in price because of availability of close substitutes thus is classified as an elastic product. In a study by Dwivedi (2002), price elasticity of demand is high when substitutes are many in the market since consumers can easily switch to other substitute products. Keeping in mind that sandals face an elastic demand, an attempt to increase price above the market price would result in low revenue. This can be illustrated in figure 1 where price and revenue of elastic product move in opposite direction.
New Product Pricing Strategies
In recognition of the fact that our company has an objective of maximizing sales especially from innovative products, we intend to utilize market penetration pricing. By setting initial price for new line of products at a low rate, our company will realize the objective to increasing market share. Penetration pricing is also favourable because of elastic nature of price elasticity of demand of our product. Besides, low cost of production favours the application of penetration pricing.
Product Mix Pricing
Our company will avail products in different lines i.e. female, male, children, and expectant mothers. All these lines have different characteristics in terms of design, material, colour, weight, and shape. When determining prices between the different products, our company will take note of customer needs and competitor prices to avoid driving away customers.
Price-Adjustment Strategies
Different price-adjustment strategies are applicable in our case. Segmented pricing, promotional pricing, and discount pricing will be used in our company. In applying segmented pricing, we intended to vary prices of products according to age, gender, social class, and characteristic of the product. To revamp sales level during special occasions like Ramadan and Eid, we will deploy promotional pricing. The strategy will also help us to clear stocks for purposes of introducing new products. Finally, slow moving products will be sold at a discount to encourage customers to purchase the product.
References
Dwivedi, D. N. (2002). Microeconomics: Theory and Applications. New Delhi: Pearson Education India.
Ferrell, O. C., & Pride, W. M. (2008). Marketing. Mason, Ohio: Cengage Learning.
Lamb, C., Hair, J., & McDaniel, C. (2008). Essentials of Marketing. Mason, Ohio: South- Western Cengage Learning.
Smith, T. (2011). Pricing Strategy: Setting Price Levels, Managing Price Discounts and Establishing Price Structures. Mason, Ohio: South-Western Cengage Learning.

