Abstract
Imperfect competition refers to a specific stiff market situation having several sellers offering heterogeneous goods and services, as opposed to a perfectly competitive market setup. The imperfect competition allows some suppliers and industries to make surplus profits. Sellers enjoy the monopolistic benefits of influencing the market price resulting in massive profits. In an imperfect market scenario, the sellers offer a non-identical product; they have the power to raise the process at any time depending on the demand for the product and service in question. Quite often, a large margin of profits attracts other business people to enter the market. An imperfect market, most of the time, leads to a monopoly market. In monopolistic competition, demand is elastic and sensitive to changes in prices.
Literature Review
Several business magazines written by different authors have diversified opinions and implications of monopolistic competition. For instance, The Guardian article explains the monopolistic type of market structure as a significant threat to the existing business democracy (Meagher, 2020). There is an escalating unease about the monopolistic situation since corporate power has lost its meaning and control over such markets. The Guardian article elucidates how economic power concentrated among a few individuals poses a great risk to the nation’s economy (Meagher, 2020). The county’s economy will be at the mercy of a few people and organizations, which is detrimental.
Subsequently, Newsweek magazine says the renowned term “monopoly” is common in some market scenarios, and it is used to frustrate consumers, as it is indicated in The Guardian article. The implications of monopoly are negative and seldom accurate. For instance, the article provides a scenario of an individual by the name of Roger Dekock who performed various transactions via his E-ZPass account in Virginia (Elliott, 2017). The customer complained about the account, terming it as a monopoly, which technically was not true. The E-ZPass company offers users different rates, and it is the choice of an individual to decide whether to use cash while paying for the toll or avoid such procedures (Elliott, 2017). However, E-ZPass appears to function as a monopoly firm to many consumers. Due to such complaints, The Guardian article explains the formulation of antitrust laws in the US to counter the monopolistic effects, which are also evident in Newsweek magazine (Meagher, 2020). The competition laws have implemented a level and fair operation across organizations within the member states.
According to a Guardian article written by Meagher (2020), the clear meaning of corporate power has deteriorated. Over successful years of unquestionable mergers and their corresponding negative impacts on the consumers, monopolistic companies have continued to thrive. They have grown bigger by spreading their networks and tentacles across numerous subcontractors and sectors of the economy hence, dictating the entire market (Meagher, 2020).
The New Yorker article expresses the same issues of certain organizations exercising dominance in the market. The magazine uses the famous Facebook Company to explain the negative impact of a monopoly market structure (Klonick, 2021). The monopolistic market structure benefits some few individuals who can afford to run their businesses while reaping huge profits, while at the same time, consumers are being frustrated by such a system.
The New Yorker magazine and the Newsweek article have a similarity when both explain how some customers’ opinions can be misleading when it comes to the impacts of monopoly market set up. For instance, Facebook was criticized when it changed its policies to enable users to keep their data after deleting their accounts (Klonick, 2021). However, during the voting on the same referendum, only 0.32 % of Facebook users agreed with the criticism (Klonick, 2021). Today Facebook has grown globally, and it has become one of the most flooded social platforms where customers use it for diversified reasons. Facebook is a monopoly company, but contrary to the Guardian article’s opinion, the New Yorker article expresses some positive impacts of a monopolistic organization.
According to the Newsweek article authored by Elliott (2017), monopolistic organizations have the ability to emerge and thrive in any market environment. The article cites Procter & Gamble after acquiring Gillette in the year 2005, controlling over 75% of the overall men’s razors (Elliott, 2017). With such an influence in the market, Procter & Gamble can frustrate customers with high prices and poor services, as the Guardian article elucidates (Meagher, 2020). Sellers who cannot sustain themselves in such an imperfect market environment due to losses are forced to exit the market.
Discussion
The different magazine represents various methods of curbing and reducing monopolistic industry. However, the process is quite challenging since the current administration system is not effective in implementing consumer protection laws (Elliott, 2017). For instance, when Facebook faced some legal suites on its online services, the board determining its proceedings was 20 in total. Each was given six-figure salaries for working for approximately 15 hours for a whole week. Then the board was managed by a different trust, which was paid 130 $ millions by Facebook (Klonick, 2021). According to Facebook, more than two hundred thousand messages from a different category of posts are approved and eligible for appeal every single day (Klonick, 2021). Therefore, countering such a monopoly structure is challenging and requires the participation of all players who control prices and profits in the economy.
From the articles, there is a clear distinction between monopoly and monopolistic competition. A monopoly is a market structure with one firm domineering and being the sole supplier. On the contrary, monopolistic competition is an example of an imperfect market having one or two suppliers selling differentiated products, but the products are not appropriate substitutes for each other (Meagher, 2020). Finding a monopolistic market is pretty simple since you only need to identify poor customer service with little or no competition at all (Elliott, 2017). The American Customer Satisfaction Index’s in the industry benchmarking scores provides reliable criteria when evaluating the market structure.
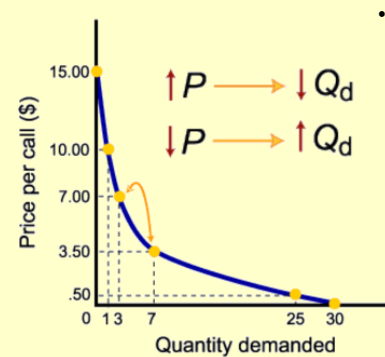
From the graph in Figure 1 above, there is evidence of an inverse or negative relationship between the price of the goods and the quantity being demanded, holding other factors constant. Therefore, the demand curve will always slope downwards since an increase in the price of any good or service in the market results in a decrease in its demand rate (Roy, 2020). Contrary, in the monopoly market structure, one seller can control the price of goods and services, hence exercising the monopolistic power in the market.
There are several strategies to eliminate monopolistic industry depending on the market structure. For instance, an individual can join an organization or a certified trade group representing a huge number of consumers hence, deploying its clout in price negotiations (Elliott, 2017). Monopolistic companies may sneer at an individual who tries finding an effective price in the market, but when a magnitude of consumers ask for discounts and better prices, they eventually cannot be ignored.
Some monopolistic corporations offer products that are not essential and basic for consumer’s survival. Therefore, consumers have the highest power, and they can decide in unison to reduce or terminate doing businesses with such monopolistic companies. In such a case, the company will have to conduct business as per the requirements of customers. The significant challenge in implementing such a strategy is the lack of collective resolution from users. Most of the federal governments endorsed with the power to protect consumers have neglected their duties. However, some governments such as California’s have continued protecting consumers’ rights (Elliott, 2017). Government is a powerful body with the full ability to safeguard consumers’ interests by eliminating monopolistic industries.
Conclusion
Imperfect competitive market structures such as monopoly and monopolistic competition are, most of the time, market environments where sellers can increase the prices at any time. An increase in prices results in enormous profits at the expense of suppressing consumers. From the articles it is evident, that imperfects competition results in poor quality of goods and services being offered at the market. Also, the economy experiences dead-weight loss since the situation costs the country’s economy when it comes to poor resources allocation. However, some opinions from the New Yorker magazine explain how Facebook is increasing customer satisfaction regardless of it being a monopoly company. Generally, the integrated value of economic operations evaluated as the sum of both consumers’ and producers’ surplus can be significant if the imperfect competitive markets conduct their operations competitively. Both the consumers and government have an obligation to eliminate imperfect competition in the market structure.
References
Elliott, C. (2017). How to avoid the new monopolies that doom consumers. Newsweek. Web.
Klonick, K. (2021). Inside the making of Facebook’s supreme court. The New Yorker. Web.
Meagher, M. (2020). Monopoly power is running wild. We need tough competition laws to rein it in. The Guardian. Web.
Roy, A. (2020). Demand, supply & market equilibrium.[PowerPoint Slides]. Web.

