Introduction
The organization where I am working is H&M as a Business Analyst, so in this task, I can prepare and develop the business strategy for H&M. To prepare the business strategy, the report is proposed, which can discuss the process and different analyses for the H&M. The main aim of this report is to develop and implement the business strategy for H&M. The report will be comprised of different sections in which the business all related aspects are discussed. The first section discussed the organization context, which contains the details about the statement of strategic content, positioning statement, and industry value chain. The second section contains information about the Porter 5 forces and the PESTEL Analysis of H&M. The third section contains the analysis of the current internal strategy followed in the H&M in the context and insight of tools. In the fourth section, the SWOT Analysis of H&M is performed. The last section contains the recommendation and conclusion in which four new strategies are proposed, along with their benefits and risks associated with them. H&M was established in 1947, and this organization will be the largest retailer of clothing around the globe. In 2014, H&M ranked 3rd in the 15th top performer companies on the supply chain of Gartner’s. H&M has 950 stores in 19 countries and ensures there is maximum control of stock using the strategy of well-established management of inventory. The main idea behind the inventory management approach of H&M retails is to enable the organization in order to achieve efficiency in cost, good productions, reduce load time for inventory along with getting a more promising market.
Organizational Context
Firm Background
H&M is a multinational fashion retail company that operates since 1947 and is headquartered in Sweden. On a global scale, the company owns 4,471 stores, 74 store markets, 51 online markets, and employs 179,000 workers; the firm’s annual revenue reaches 233 billion SEK in net sales (About H&M Group 2020). The company occupies a solid position among its competitors in the retail and fashion industry. Since the company operates globally, its biggest rivals are also multinational companies that have a large market share. They include Zara, Uniqlo, Gap, ASOS, Macy’s, and others (Top 13 H&M Competitors 2018). The long history of operation has contributed to the firm’s strategic planning.
Statement of Strategic Intent
The H&M works by the statement of strategic intent, which implies providing the customer with quality fashion at a reasonable rate or price. H&M’s mission is to make fashion and design accessible to everyone; the firm’s vision is to lead positive change in the industry by providing renewable and circular products maintaining sustainability and equality in the company (About H&M Group 2020). The company’s values include teamwork, belief in people, entrepreneurial spirit, constant improvement, cost-conscious, open-mindedness, and simplicity (About H&M Group 2020). With quality, the organization makes sure that the product is manufactured ethically and environmentally. The company’s goals include leading the change by means of innovation, maintaining circular and climate positive production, and being a fair and equal workplace (About H&M Group 2020). As an organization, H&M feels the responsibility to all of them who contributed with them to achieve success. This result can be closely committed to H&M working with the suppliers and business partners, which assist the organization in attaining ethical practices and long-term sustainability throughout the manufacturing factories within the organization and aspects of business operations. Some of the key issues are outlined in the Statement of the strategic intent of H&M, which are safety, child labor, rights of workers, etc. (MacIntosh 2015). H&M doesn’t allow child labor, organization15 age of the youngster, which is the legal employment age. While addressing safety organization ensure all building and work area is safe for all their workers and safety is the top priority of H&M. Also, the right of workers is very important within the organization, and there is no decimation towards any individual; the organization promotes diversity, which can improve the organization’s productivity and effectiveness. This way, the organization’s strategic intent is enhanced.
Positioning Statement
A position statement of H&M is an expression about how H&M products can fulfill the needs and expectations of customers by following the way which cannot be followed by another competitor. Positioning is the process that assists the organization in identifying the market niche appropriately for the product and getting established in an area. There are four basic elements of a positioning statement (Marketing Strategy of H&M 2019). Audience Targeted, Customer FOR (Frame of Reference) in which brand will compete with others and core prospect demographics, and attitudinal description. H&M offers accessible and renewable fashionable clothing to the diverse population of the middle class to lead the change in the fashion retail industry toward equality, fairness, and sustainability.
H&M positioning statement includes:
- Fast Fashions for everyone or every person at low cost or prices, can help the organization to grab the maximum market and generate high revenue and profit.
- Tailor ads to the segments of geography and demographic.
Industry Value Chain
The value chain of H&M is collected to the unlimited ecosystem, people, and communities as well as other businesses around the globe, which main the organization will be the part of the economy globally. The organization’s social economic and environmental impact is far-reaching and significant, and the organization wants it to be as positive as possible. This means to create a positive change in the industry value chain from factories and farms which supply to the millions of customers can be done by organization own-self (Circularity and Our Value Chain 2020). H&M Strategy is grounded on the idea it can be used to leverage the change in business scale and size in the industry and to create the maximum positive impact along with reducing the negative impact (Impacts Along Our Value Chain 2019). The particular area focus is the improvement and protection of human rights along with the industry value chain. The industry value chain also includes sustainability, which starts while drawing the board. H&M needs to create and develop fashion without compromising on quality, design, sustainability, and prices. The choice of design and material impact the clothing industry and people who buy and sell as well as wear clothes. H&M can make its impact more positive by reducing all negative impacts and by choosing sustainable materials.
External Strategic Analysis
The external strategic analysis helps out H&M stay on top of trends in the clothing industry, which may affect the organization but can be out of control. In the External Strategic Analysis, two tools are used to completely analyze the organization’s current external environment.
Porter 5 Forces
The Porter 5 forces are used to understand the force which can shape the competition of H&M in the industry. It can also be used to help to adjust to the H&M strategy, which can suit the competitive environment and improve the profit and revenue potential. Here below are the Porter 5 forces analysis of the H&M is given, which can determine the profitability and competition intensity that can be expected in the retail sector of fashion (Courtney 2013).
As illustrated in the table, H&M operates in an industry that is characterized by a high level of rivalry intensity. The rapidly changing consumer tastes require a timely response from the retailers, which is why competitors generate new trends and initiate new lines of clothing. Also, the competition requires increased investment in advertising campaigns to ensure H&M’s presence in the market. At the same time, the threat of new entrants is considered low since to obtain a competitive advantage; new entities need to have a large capital. H&M’s brand recognition and the overall long-term favorable reputation and customer loyalty contribute to its stable position in the market. The buyers have a moderate level of bargaining power because fashion trends are mostly generated by brands. Moreover, the wide range of products available from the company allows for meeting the needs and requirements of multiple populations that minimizes the need for bargaining. On the other hand, the bargaining power of suppliers is considered low because the firm requires only materials supplies. The origin of the materials has no impact on consumer choice or brand recognition; on the contrary, it is the brand that produces the ultimate product. Finally, the substitution threat is low due to the solid position of the firm in the industry and a significant market share. H&M is one of the leaders in the fashion industry that aligns its decision-making with the buyers, which is why there are limited companies that might substitute the firm. Among the most competitive brands are G-Star and GAP.
PESTEL Analysis
PESTEL/PESTLE Stands for Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, and Legal. A PESTEL analysis is the tool or framework used by the H&M marketer to monitor and analyze the external market environment or macro-environmental factors which strongly impact the organization. Its results have a twofold impact on organizational decision-making: environment identification and the provision of information that allows the company “to predict situations and circumstances that it might encounter” (Yuksel 2012, 53). The result of PESTEL analysis is used for the identification of weaknesses and threats, which can be later used in the SWOT Analysis (Courtney 2013). However, the PETSEL Analysis of H&M is given below.
As illustrated in the table, the political environment in which H&M operates is characterized by deglobalization trends and instability in the leadership of the leading countries of the world. Also, the legislation aimed at restricting trade in North America obstructs H&M’s presence in those markets and diminishes global expansion opportunities. From an economic point of view, the changes in Asian markets’ taxation, economic crisis-induced sales changes, and shifts in labor laws all contribute to the instability and uncertainty of the firm’s operations. Social factors such as social media impact growth, and shifts in customer demands trigger the responsive changes in H&M’s strategic planning. Similarly, technological advancement imposes both challenges and opportunities for production automation and sales increase. Legal procedures regulating retail are strict in some countries and diminish H&M’s presence in their markets. Finally, the environmental awareness trend influences customer choices and requires an adequate response from the firm’s side.
Internal Strategic Analysis
This analysis helps to explore the competency of H&M, competitive viability, and cost position in the marketplace. By conducting the internal strategic analysis, H&M often provides the measure of user information. Usually, this analysis refers to the internal growth of the organization by using the resources (internal). The analysis focused on developing the new product along with hiring the right people, increasing efficiency and effectiveness, and improved or enhanced marketing (Marr 2006).
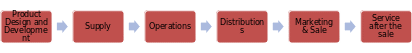
Firm Value Chain
Derived from the industry value chain outlined earlier in the report, the firm value chain includes a set of activities that ensure added value at each stage of product utilization. H&M’s firm value chain contains a linked set of value creation activities that begin with the basic raw materials coming from the supplier and move towards activities that are value-added in a sequence. Those activities are involved in producing and marking the product and ending with the supplier to get the final goods in the hand of the consumer ultimately (Milberg, n.d.). This can allow H&M to understand the operations which can create the value and the firm can use for:
- Understanding their position of cost.
- The identification of multiple means which can be used to facilitate and support the implementation of the business-level strategy chosen.
- Activities of the firm value chain of H&M include (Product Design and Development, Supply, Operations, Distributions, Marketing & Sale, Service after the sale, etc.). These elements of H&M’s value chain are of critical importance since they define the alignment of the company’s overall operations with its mission, vision, and goals. The firm’s value chain “is connected to countless people, communities, ecosystems, and other businesses around the world” and prioritizes climate-friendly manufacturing (Circularity and Our Value Chain 2020). Therefore, the opportunity to reuse and recycle all garments and fabrics used and produced by H&M add to the product value.
- For the source of competitive advantage, H&M should be allowed for capability or resources.
- To perform the activity in such a way that competitors of H&M are performing.
- To perform the activity of value-creating, which cannot be completed by competitors.
Swot Analysis
SWOT Stands for Strength, Weakness, Opportunities, and Threats. This will be a useful and simple tool to analyze the strength and weaknesses of H&M as well as opportunities and threats that the organization may face. It can help H&M to focus on the strengths, reduce the threats, and take the competitive advantage of the opportunity available to the organization (Birnik 2008). Here below the SWOT Analysis of H&M is given:
Recommendations
To improve the performance over the next four years, I would recommend the following four strategies to the top management of H&M:
- Increase sales on a global level: It is important to plan for the future and always think about the externalities in mind. Having a globalized and macro vision can help top management to understand new trends that may arise at any time. Looking outside the organization and having a third-part would look inside will be the right way to implement a business model to fit the latest trends, ensuring performance in the market competition.
- Benefits:
- Generate high revenue and profit
- Follow the latest trends to improve the brand value
- Risks:
- Failure of the business
- Time is taken and delay in business operations.
- Benefits:
- Determine three to five business priorities: Those who have more than five goals cannot achieve the outcome, and actually, they do not have any goal. This will be because they want to change a lot of things at the same time, and this is very difficult to improve performance (Hibberd 2015). Choosing 3 to 5 clear and objective goals, which are prioritized and a purse can certainly be achieved. The strategy to improve the performance is based on priority choice.
- Benefits:
- Businesses can achieve the goals and objectives very fast
- Performance is enhanced and improved
- Risks:
- Stuck in confusion when objectives are more than five
- Failed to achieve the objectives
- Benefits:
- Employ talented staff: The firm needs to choose the right people at the right place, integrated with operations and strategy. This point understands how culture would be determinant as a strategy to improve business performance.
- Benefits:
- Productivity is increased and enhanced
- Work done will be efficient and according to requirements
- Risks:
- Turnover of workers or employees
- The conflict between employees and workers
- Employees or workers leave during half of work
- Benefits:
- Initiate a feasible performance monitoring system: Monitors the performance of the organization periodically as this is the best rule of management.
- Benefits:
- Defects easily recognized
- Role of worker and employee is demonstrated
- Progress of work is tracked
- Risks:
- Delay in work and negative variance in the performance
- Cost overruns
- Benefits:
References
“About H&M Group.” H&M Group. Web.
Birnik, Andreas, and Richard Moat. “Developing actionable strategy.” Business Strategy Review19, no. 1 (2008), 28-33.
“Circularity and Our Value Chain.” H&M Group. Web.
Courtney, Roger. “Strategic Analysis: The External Environment.” Strategic Management in the Third Sector, 2013, 93-108. Web.
Hibberd, Gary. “Developing a BCM Strategy in Line with Business Strategy.” The Definitive Handbook of Business Continuity Management, 2015, 23-30.
“Impacts Along Our Value Chain.” Sustainability Reporting.
MacIntosh, Robert, and Donald MacLean. “Strategic Intent.” Strategic Management, 2015, 46-54. Web.
“Marketing Strategy of H & M – H & M Marketing Strategy.” Marketing91.
MARR, B. “Internal strategic analysis — resource-based view.” Strategic Performance Management, 2006, 39-61. Web.
Milberg, William, and Deborah Winkler. “Lead Firm Strategy and Global Value Chain Structure.” Outsourcing Economics (n.d.), 103-156. Web.
“Top 13 H&M Competitors.” Marketing91.
Yuksel, I. “Developing a Multi-Criteria Decision Making Model for PESTEL Analysis.” International Journal of Business and Management, 2012, 7 (24): 52-66.

